RELIANCE provides a suite of innovative and interconnected services integrated into the EOSC and used by the EOSC scientific communities to support thematic and multidisciplinary research in Earth Science.
About
RELIANCE has recently extended the EOSC’s capabilities with a set of advanced research enabling services for the open, efficient, and cross-disciplinary management of the research lifecycle, supporting the adoption of FAIR and Open Science practices, particularly in Earth Science communities.

RELIANCE services enhance the discovery of and access to research data, including EO datasets (Copernicus), extract relevant knowledge from scientific text, and manage the research lifecycle holistically. Researchers in RELIANCE come from three different Earth Science communities, including:
- Sea monitoring community (represented by CNR-ISMAR – Italy): Marine ecologists, biologists, geologists, geophysicists, geochemists and oceanographers studying past and present dynamics of the ocean and the ocean-atmosphere interface
- Climate change community (represented by University of Oslo – Norway): Earth scientists working on climate impact studies, climate mitigation and adaptation, geo-engineering, monitoring
- Geohazard community (represented by INGV – Italy): Earth scientists working on improving geohazard scientific research and assessment, with scientific knowledge of volcanic and seismic Supersites, in support of Disaster Risk Reduction
RELIANCE implemented a research lifecycle management service ecosystem that relies on RO-crate-based research objects (ROs) as the overarching mechanism to manage scientific research activities, leveraging the ROHub platform as the reference service. ROs rely on Data Cubes for efficient and scalable EO data access and discovery via the Advanced geospatial Data Management (ADAM) platform and on text mining services based on expert.ai’s AI-based NLP/ U platform to extract and enrich research objects with machine-readable metadata from scholarly communications and other scientific text.
RELIANCE services allow researchers to continue doing their science as usual, but now being able to access larger datasets, including EO data from heterogeneous sources, share their results more easily, having all resources accessible via a single entry point and doing Open Science by default.
Challenge
One of the key challenges regarding the adoption and implementation of Open Science practices, though, is enabling the reproducibility of results to support trust in science. Besides being able to access scientific knowledge, publications and research data, the replicability and reproducibility of research results is one of the main goals of Open Science. In fact, reproducibility is one of the key ambitions of the EU’s open science policy. However, as is evidenced in different studies in the literature, reproducibility of research results, even those published in prominent journals, is in most cases not possible. This so-called reproducibility crisis is a serious issue affecting many scientific studies. A survey from 2016 by Nature on 1,576 researchers found that more than 70% of researchers from different disciplines have tried and failed to reproduce another scientist’s experiment results, including 64% of earth and environmental scientists. More than half of all researchers have failed to reproduce their experiments. Even more recent studies like a 2019 study in scientific data estimated with 95% confidence that of 1,989 articles on water resources and management published in 2017, only 0.6% to 6.8% of results might be reproduced, even if each of these articles provided sufficient information that allowed for replication.
To support the reproducibility of research results, particularly in communities like Earth Science, researchers and/or reviewers need to be able to access not only the data used to produce the results but also the methods and/or code used to process the data and generate the results, and any relevant documentation and explanation of the research (e.g., paper, presentations, etc.). Additionally, to facilitate the reproducibility of these results, researchers should be able to easily reproduce the computing environment where these methods/codes were executed. As stated in this lecture, in computational / data science, a particular analysis, calculation, or notebook may depend on hundreds of different software packages, each with many different versions. The reproducibility of produced results depends on having the correct version of these packages.
The solution
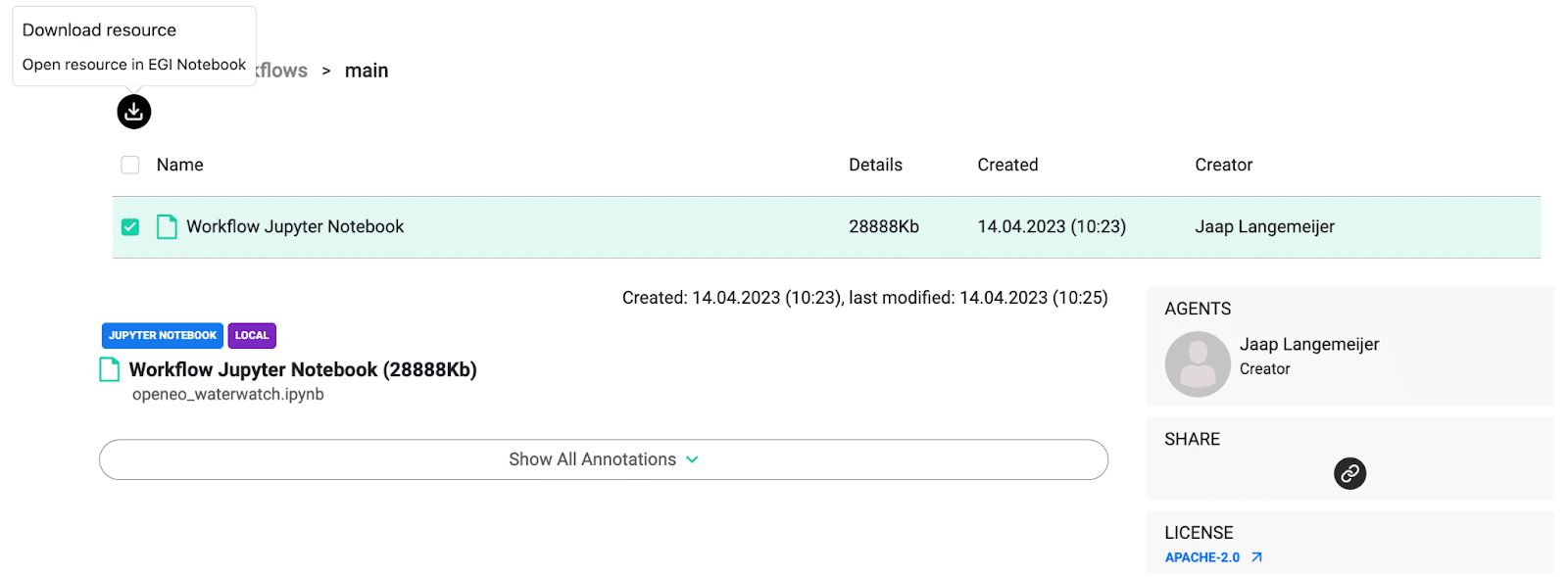
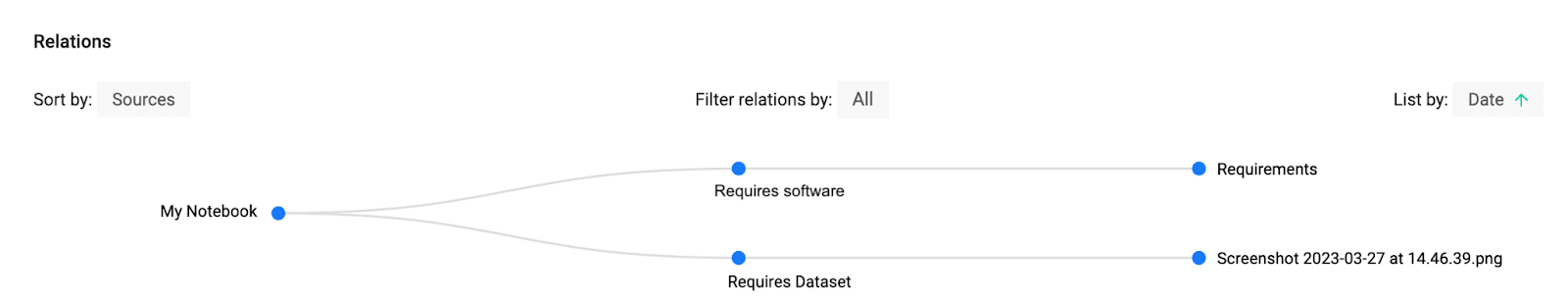
To address all these challenges, RELIANCE has leveraged and integrated various EGI services with ROHub, the RELIANCE platform for managing RO-crate Research Objects. ROHub enables researchers to aggregate and manage via Research Objects all thea resources, typically distributed across different repositories/locations, related to a particular study/research, providing an integrated view over fragmented resources using PIDs and metadata. The RO provides the single entry point for researchers to access the data, the methods/code, publications, etc., related to particular research. But to enable an easy reproducibility of these methods/codes, it is necessary to allow researchers to access and reproduce the computing environment easily from the Research Object itself in ROHub. As one of the most commonly used computing environments to carry out data analysis/processing in Earth Science is via Jupyter Notebooks, ROHub leverages and integrates the following EGI services:
EGI Notebooks: a browser-based tool, based on JupyterHub, for interactive analysis of data using EGI storage and compute services. RELIANCE researchers can open and load their Jupyter notebooks in their ROs automatically in Notebooks directly from ROHub and execute their methods/processing in an interactive computing environment. To use this feature, the notebook(s) in the RO must have been assigned type “Jupyter Notebook”.
EGI Replay: a place, based on Jupyter Binder, to reproduce notebooks and their run-time environment. Complementing the previous functionality, researchers with Replay can open and load automatically their Jupyter notebooks and reproduce their associated computing environment, including any related input datasets, directly from their ROs in ROHub. To use this feature, the notebook(s) in the RO must have been assigned type “Jupyter Notebook”, and it should be connected with the run-time requirements file (e.g., requirements.txt or requirements.yml) and any required input data/resource.
EGI Datahub: allows users to bring data close to computing to exploit it efficiently and/or to publish and share data. DataHub is integrated with Notebooks/Replay, and thus, RELIANCE researchers can access it once they have loaded their notebooks from ROHub. Datahub is used in RELIANCE mostly to easily share resources among the RELIANCE research communities through a dedicated Virtual Organization. Resources created in DataHub can then also be easily aggregated and shared via ROs.
Services provided by EGI
Supporting projects
EGI-ACE is a 30-month project with a mission to empower researchers from all disciplines to...